Slides
ruby command-line tools
When you use Ruby you will encounter an entire ecosystem of tools, most of which are run from the command line. This section gives a brief overview of the most important of these tools.
Ref: WGR Chapter 1. Bootstrapping your Ruby literacy
ruby
-
rubyis the Ruby Interpreter -
ruby hello.rbruns the Ruby source filehello.rb - Options
-
-w- warnings -
-v- version or verbose --help-
-c- check syntax
-
irb
- Interactive Ruby Browser
- aka "the ruby console"
- interprets Ruby one line at a time
- REPL: Read Eval Print Loop
uncluttering irb's cluttered prompt
irb --simple-prompt
or
alias irb="irb --simple-prompt"
or
echo "IRB.conf[:PROMPT_MODE] = :SIMPLE" >> ~/.irbrc
ri and rdoc
-
if you're running
rvm, do this right now:rvm docs generate -
rdoc generates and displays documentation
- per file or class or gem
- documentation comes from inside source code
- RDoc Syntax described at http://rdoc.rubyforge.org/RDoc/Markup.html
web docs
- ruby-doc.org
- gotapi.com/rubyrails
- api.rubyonrails.org
-
gem serverlaunches an rdoc browser locally - railscasts.com
- destroyallsoftware.com
cheat
- a text-only command-line wiki
-
gem install cheatfor command-line tool or see http://cheat.errtheblog.com$ cheat agile Agile Manifesto_____________ - Individuals and interactions over processes and tools - Working software over comprehensive documentation - Customer collaboration over contract negotiation - Responding to change over following a plan While there is value in the items on the right, we value the items on the left more.
rake
- one
Rakefilecontains many "tasks" which can be run a larake test - rake looks up the directory tree for a Rakefile
-
rake --tasksshows all defined tasks in the current Rakefile- also
rake -T
- also
gem
- aka RubyGems
- gem = Ruby package = library or program or plugin
-
gem install foo- downloads and installs the "foo" gem from rubygems.org -
gem,rvmandbundlerlive in uneasy harmony
gem plugins
- installed as gems, but extend the
gemcommand -
for example,
open_gemwhich opens the source code for a gem in your editorgem install open_gem gem open rake
bundler
- manages lots of different sets of gems and versions thereof
- bundler is a gem itself
-
gem install bundlerloads it into the current gemset
-
bundle installbundle update-
Gemfilelists all the gems for the current project (directory)- similar to
Rakefilein scope
- similar to
rvm
- Ruby Version Manager
- manages lots of different versions and distros of Ruby on a single computer
rvm listrvm install 1.9.2rvm use 1.9.2
- also manages gemsets
rvm gemset create teachingrvm use 1.9.2@teaching
- overlaps with
gemand Bundler- in sometimes odd ways
Bundler vs. RVM
- RVM manages multiple gemsets on a single machine
- Bundler manages the same gemset on multiple machines
RSpec
- testing framework
- describe, it, before, after, should
dotfiles
-
Are you on Unix/OSX? Check out Alex's dotfiles repo
git
Git is a Distributed Version Control System. It's very popular these days, especially among Ruby developers.
Git allows offline, asynchronous, decentralized development.
GitHub is a web service built on git that also adds issue tracking, automated pull requests and merging, etc.
git workflow
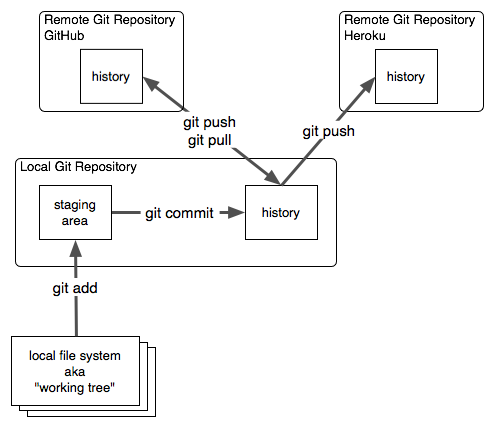
git cheatsheet
-
git init-- create a repo locally -
git clone-- copy a repo from a server -
git status-- what has changed -
git log-- history -
git add-- stage files for commit (*local*) -
git commit-- commit staged files (*remote*)
See also nerdgirl's visual git cheatsheet at https://github.com/nerdgirl/git-cheatsheet-visual
Git Configuration
Git needs to know who you are, so try this:
git config --global --list
and if it doesn't have your name, do this:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email mail@example.com